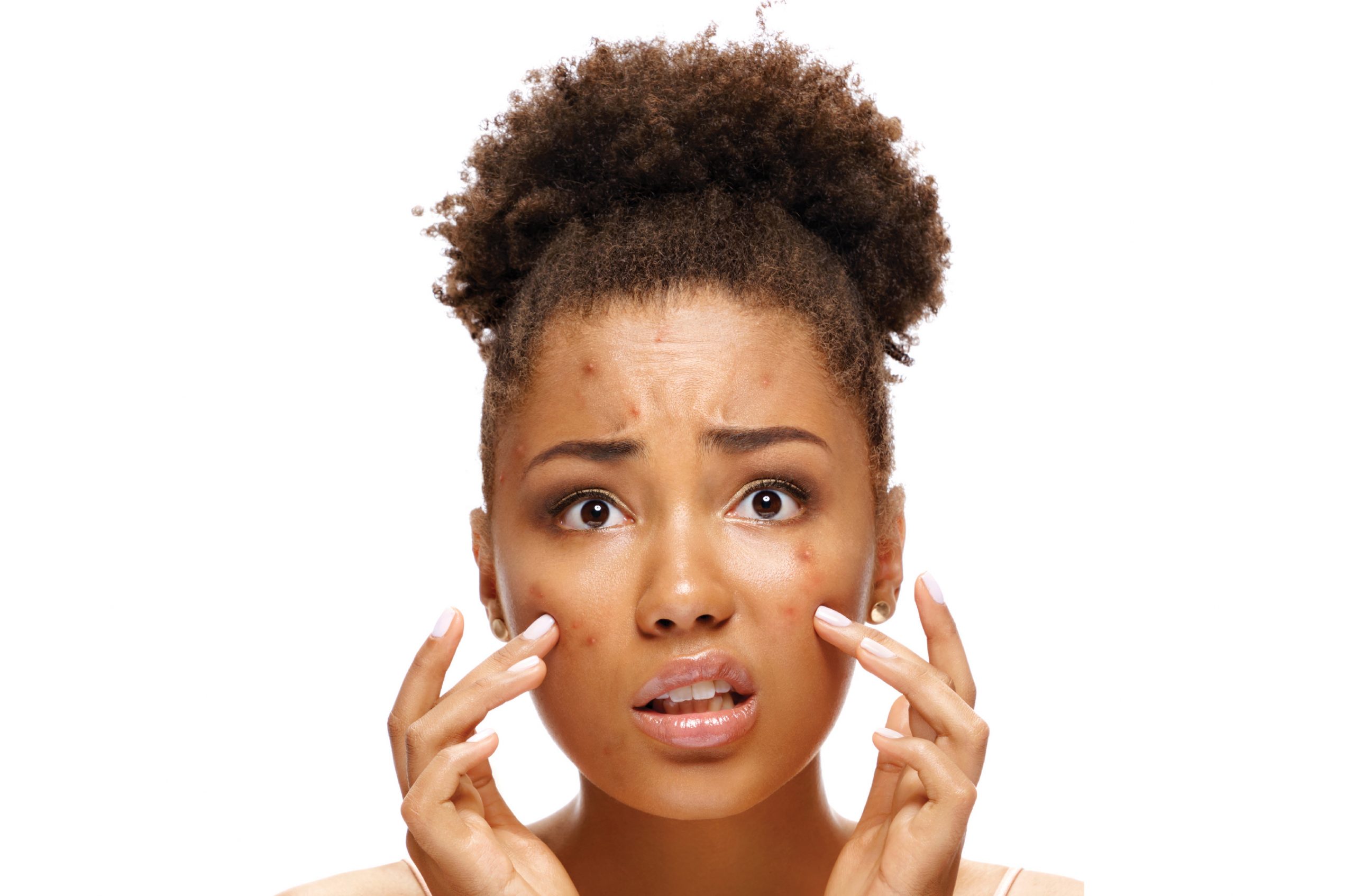
Is there anything that deflates your confidence more than noticing a facial blemish in the mirror? While our instinct may be to poke, prod and pop to make the unsightly spot go away, most of the time, it’s better to just let it be. To know the best steps to prevent and treat any blemish, it’s important to first understand what exactly is going on with your skin.
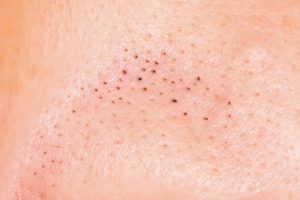
blackhead
How to spot it: This mild form of acne gets its name from its black or dark appearance. Unlike pimples, blackheads are not inflamed, so they are not painful.
What causes it: Blackheads form when the openings of hair follicles clog up. A bump called a comedo is created by dead skin cells and oil collecting in the opening. If the skin over the bump opens, the exposure to air causes it to appear black.
How to treat it: You can prevent blackheads by regularly washing your face, using products that are noncomedogenic and exfoliate your skin.
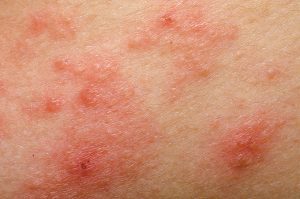
eczema
How to spot it: Symptoms vary from person to person. Common signs include thickened scaly skin, dry skin, red to brownish-gray patches, and raised bumps that may leak fluid and scale over when scratched. Eczema is common on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids and inside the bend of elbows and knees.
What causes it: Eczema is caused by a gene variation that affects skin’s ability to retain moisture and protect you from bacteria, irritants and allergens. This leaves skin more vulnerable to environmental factors.
How to treat it: Take shorter showers, using warm instead of hot water, and moisturize your skin at least two times a day. It’s also helpful to identify triggers that worsen the condition, so you can avoid them. Common triggers include sweat, stress, obesity, soaps, detergents, dust and pollen.
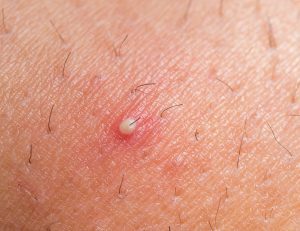
ingrown hair
How to spot it: Like acne, these blemishes appear to be red or raised bumps. They also may cause a small pus-filled blister.
What cases it: Ingrown hairs are caused by the hair growing sideways into your skin instead of toward the surface. This often results from hair curling inwards after a shave, tweeze or wax. It is often caused by clogged pores.
How to treat it: Oftentime, an ingrown hair will go away on its own. To avoid them forming, wash your face daily to prevent pores from clogging. Try improving your shaving technique by shaving in the direction your hair is growing. Using shaving cream and applying after shave moisturizer also can treat ingrown hairs.
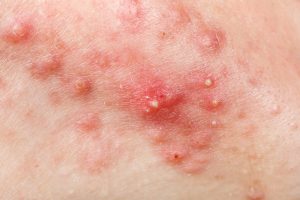
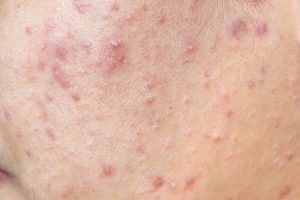
papules and pustules
How to spot it: Papules are small raised bumps on the skin that appear inflamed. They do not contain any pus. Pustules are red tender bumps that contain pus at their tips.
What causes it: When a clogged pore becomes infected and inflammation spreads, it can create a papule or pustule.
How to treat it: Don’t pick at the inflamed area or try to pop the blemish because that may spread the infection. Gently wash the affected area twice a day and stay away from irritants. If regularly cleansing does not stop breakouts, consult your doctor for medical treatment options.
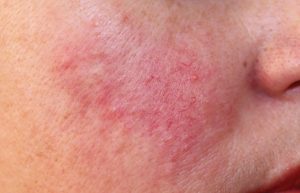
rosacea
How to spot it: The key symptoms for the conditions are facial redness with swollen red bumps and small visible blood vessels.
What causes it: The cause of rosacea is unknown. It may result from an overactive immune system, heredity, environmental factors or a combination of these.
How to treat it: Treatment should be focused on controlling the symptoms. Along with medical intervention, laser therapy can remove visible blood vessels, and opting to use skin care products that cause less irritation can reduce redness. It also is important to protect your skin from the sun.
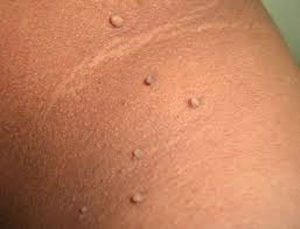
skin tag
How to spot it: These common skin growths are characterized by a short piece of skin that sticks out. They are often painless but may become irritated if they chafe against clothing or something else.
What causes it: Skin tags are formed when extra cells grow in the top layers of the skin. They tend to develop when the skin rubs against itself.
How to treat it: Most skin tags are harmless and can be left alone. However, if the appearance is unwanted or it’s located in an area that becomes irritated, it can be surgically removed or frozen off by a medical professional.
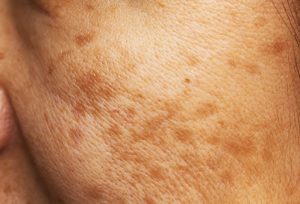
sunspot
How to spot it: Also known as liver or age spots, these blemishes are characterized by flat brown patches.
What causes it: Sunspots are hyperpigmentation caused by ultraviolet light speeding up the production of melanin. After years of sun exposure, spots appear in areas where melanin becomes clumped.
How to treat it: In most cases sunspots are harmless, but be sure to consult a medical professional to make sure they are not a cancerous lesion. To reduce age spots appearance, there are several options, such as microdermabrasion, laser therapy, chemical peels and cryotherapy.
whitehead
How to spot it: These blemishes appear as skin colored spots or bumps. On lighter skin, they may appear to have a white center surrounded by a red halo. While for darker skin, the halo may appear a darker or more purple hue.
What causes it: Like blackheads, whiteheads are formed by clogged pores. If the skin over the comedo that forms remains closed, it stays white. Excess oil production also can cause acne flares.
How to treat it: Like other acne, avoid picking or popping whiteheads. To prevent them, opt for oil-free, non-clogging skin care and makeup and regularly wash your face with a gentle cleanser.
Sources: Healthline, Mayo Clinic